Save Sensor Data (non-GenDC)
In this tutorial, we will learn how to save GenDC data transferred from a sensor into a binary file. If your device data format is GenDC, and if you prefer to save a whole GenDC container instead of only image data, see the previous tutorial page Save Sensor Data (GenDC).
Prerequisite
- ion-python
pip3 install -U pip
pip3 install ion-python==1.8.10
Tutorial
In previous tutorials, we utilized a single building block (BB) in a pipeline to acquire sensor data. Now, we're incorporating the binarysaver BB to enable a two-step flow: 1. Acquiring data, and 2. Saving data within the pipeline.
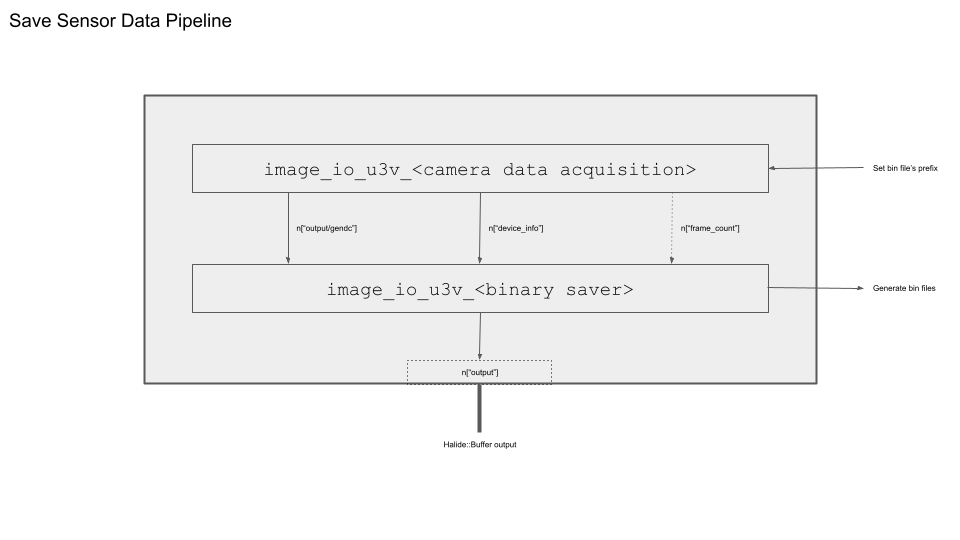
Build a pipeline
The process of initializing the pipeline Builder is exactly the same as in the previous tutorials.
# pipeline setup
builder = Builder()
builder.set_target('host')
builder.with_bb_module('ion-bb')
As the succeeding building block (BB) after the sensor data acquisition BB, we connect the binarysaver BB to establish the flow: 1. Acquire data, then 2. Save data in the pipeline.
The specific building block (BB) utilized depends on the type of sensor data being used. In this tutorial, we present an example demonstrating how to save Mono12 image data. If your device data format is GenDC, and if you prefer to save a whole GenDC container instead of only image data, see the previous tutorial page Save Sensor Data (GenDC).
| Data Acquisition BB | Binary saver BB | |
|---|---|---|
| non-GenDC | image_io_u3v_cameraN_u<byte-depth>x<dim> | image_io_binarysaver_u<byte-depth>x<dim> |
| non-GenDC (e.g. Mono8) | image_io_u3v_cameraN_u8x2 | image_io_binarysaver_u8x2 |
| non-GenDC (e.g. Mono12) | image_io_u3v_cameraN_u16x2 | image_io_binarysaver_u16x2 |
| non-GenDC (e.g. RGB8) | image_io_u3v_cameraN_u8x3 | image_io_binarysaver_u8x3 |
We are now adding two BBs to our pipeline builder. The second BB, image_io_u3v_cameraN_u16x2, requires five inputs for its ports: Image data, Device Information, and framecount, image width and height.
# set port
width_p = Port('width0', Type(TypeCode.Int, 32, 1), 0)
height_p = Port('height0', Type(TypeCode.Int, 32, 1), 0)
# bind input values to the input port
width_p.bind(width)
height_p.bind(height)
# add the first BB to acquire data
node = builder.add("image_io_u3v_cameraN_u16x2")
# add the second BB to save binary data
node_sensor0 = builder.add("image_io_binarysaver_u16x2").set_iport([node.get_port('output')[0], node.get_port('device_info')[0], node.get_port('frame_count')[i], width_p, height_p ])
Image data, Device Information, and framecount are obtained by the acquisition BB in the previous node, image_io_u3v_cameraN_u16x2. The width and height can be retrieved using the command arv-tool-0.8 -n <device name> control Width Height in the console. For detailed usage instructions, please refer to arv-tool-0.8.
For non-GenDC data
For multi-sensor data
If you acquire data from more than one sensor in the first BB using Param("num_devices", 2), you must save them separately using individual binary saver BBs. Otherwise, the data from one sensor will overwrite the data from the other.
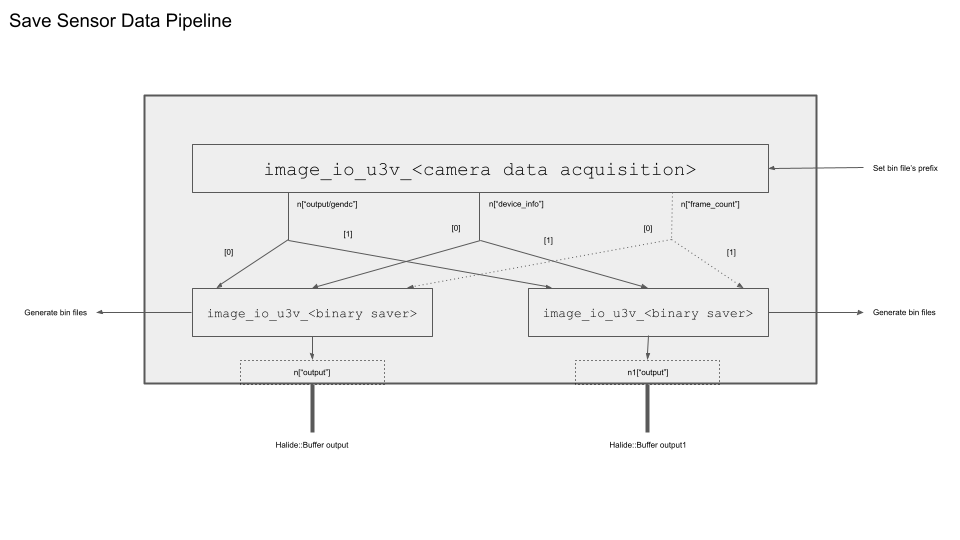
To access the output data from each sensor in the first BB, you can use indexing [] as follows. Ensure that you set Param("prefix", "image0-") and Param("prefix", "image1-") for each binary saver BB to prevent them from overwriting each other's content.
width_ps = []
height_ps = []
for i in range(num_device):
width_ps.append(Port('width' + str(i), Type(TypeCode.Int, 32, 1), 0))
height_ps.append(Port('height' + str(i), Type(TypeCode.Int, 32, 1), 0))
...
if num_device ==2 :
t_node1 = builder.add("image_io_binarysaver_u16x2") \
.set_iport([node.get_port('output')[1], node.get_port('device_info')[1], node.get_port('frame_count')[i], width_ps[1], height_ps[1]])
.set_param([output_directory,
Param('prefix', 'image1-')])
# create halide buffer for output port
terminator1 = t_node1.get_port('output')
output1 = Buffer(Type(TypeCode.Int, 32, 1), ())
terminator1.bind(output1)
If we have multiple devices, make sure that each payloadsize matches and bound respectively:
# bind input values to the input port
for i in range(num_device):
width_ps[i].bind(width[i])
height_ps[i].bind(height[i])
Set output port
The binary file will be saved within the binary saver BB process, while we obtain a scalar output from the pipeline.
This is merely a terminal flag to indicate whether the BB successfully saved the data or not, so the specific value inside may not be of concern. We simply need to create an output buffer to receive it.
# create halide buffer for output port
terminator0 = node_sensor0.get_port('output')
output0 = Buffer(Type(TypeCode.Int, 32, 1), ())
terminator0.bind(output0)
Execute the pipeline
Execute builder.run() to finish the pipeline as usual.
By default, the binary data will be saved in the following format: <output directory>/<prefix>0.bin, <output directory>/<prefix>1.bin, <output directory>/<prefix>2.bin, and so forth. The default output directory is the current directory, and the default prefix is raw-. To customize these values, please utilize the Param within the binary saver BB.
Complete code
Complete code used in the tutorial is here.